ما هو ال seo: Powerful Terms That Help You Boost Your Website
This comprehensive SEO glossary explains the essential terms, acronyms, and concepts used in search engine optimization and digital marketing today. It’s organized alphabetically for easy reference and covers everything from the basics to advanced strategies.
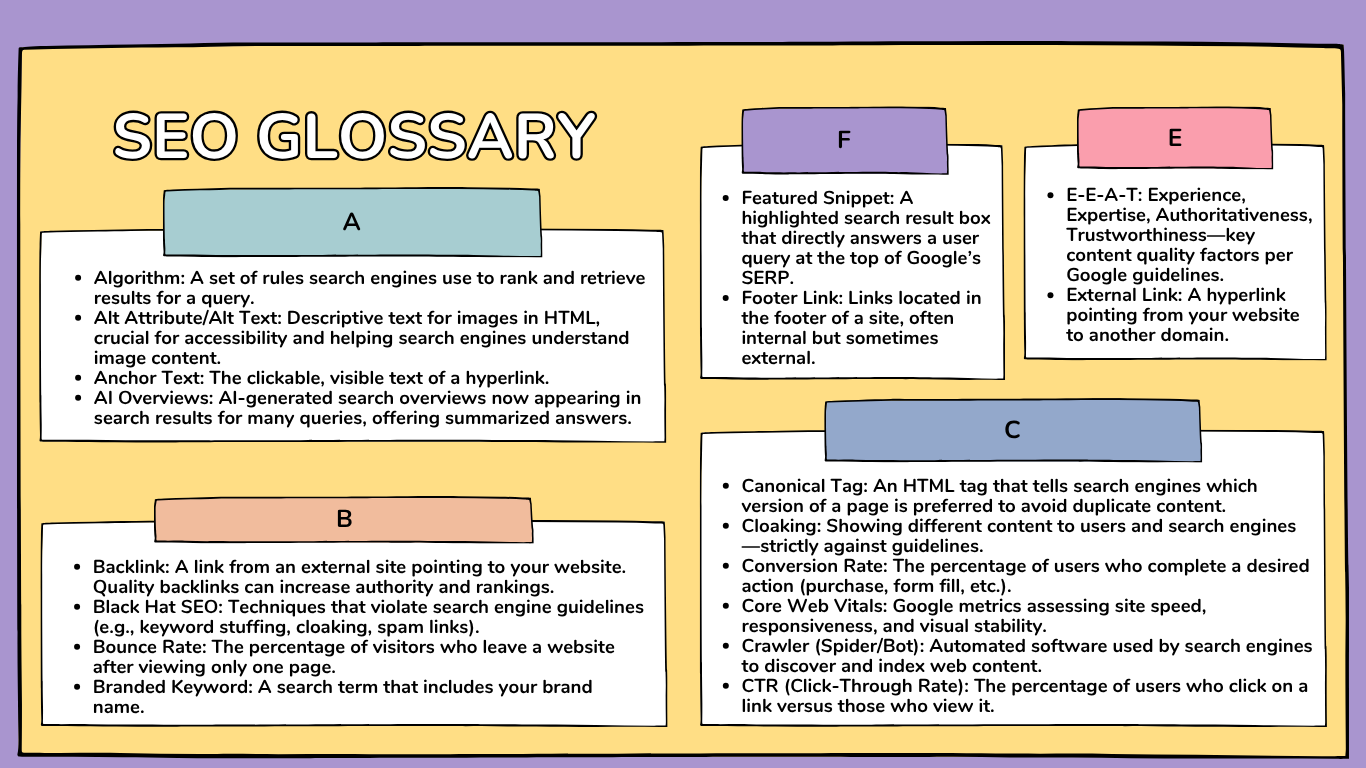
A
Algorithm
A set of rules search engines use to rank and retrieve results for a query.
Alt Attribute/Alt Text
Descriptive text for images in HTML, crucial for accessibility and helping search engines understand image content.
Anchor Text
The clickable, visible text of a hyperlink.
AI Overviews
AI-generated search overviews now appearing in search results for many queries, offering summarized answers.
B
Backlink
A link from an external site pointing to your website. Quality backlinks can increase authority and rankings.
Black Hat SEO
Techniques that violate search engine guidelines (e.g., keyword stuffing, cloaking, spam links).
Bounce Rate
The percentage of visitors who leave a website after viewing only one page.
Branded Keyword
A search term that includes your brand name.
C
Canonical Tag
An HTML tag that tells search engines which version of a page is preferred to avoid duplicate content.
Cloaking
Showing different content to users and search engines—strictly against guidelines.
Conversion Rate
The percentage of users who complete a desired action (purchase, form fill, etc.).
Core Web Vitals
Google metrics assessing site speed, responsiveness, and visual stability.
Crawler (Spider/Bot)
Automated software used by search engines to discover and index web content.
CTR (Click-Through Rate)
The percentage of users who click on a link versus those who view it.
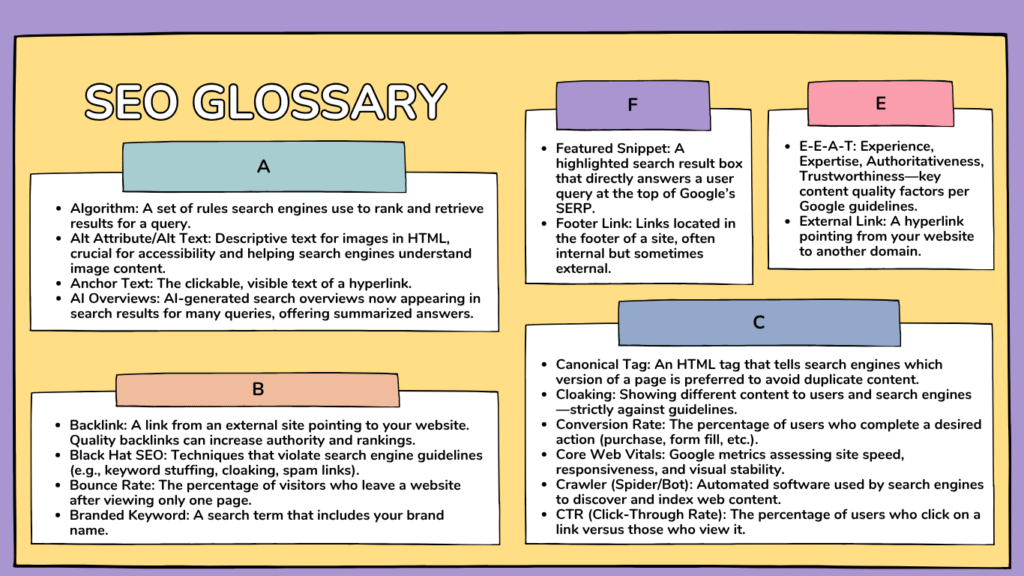
D
De-indexing
Removal of a page from a search engine’s index.
Disavow Tool
A feature in Google Search Console to instruct Google to ignore specific backlinks.
Domain Authority
A score predicting how well a website is likely to rank on SERPs, based on link profile and other signals.
Duplicate Content
Content that appears in more than one location online, which may harm ranking.
E
E-E-A-T
Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness—key content quality factors per Google guidelines.
External Link
A hyperlink pointing from your website to another domain.
F
Featured Snippet
A highlighted search result box that directly answers a user query at the top of Google’s SERP.
Footer Link
Links located in the footer of a site, often internal but sometimes external.
G
Google Analytics
Google’s tool for tracking and reporting website traffic and user behavior.
Google Search Console
Free tool for monitoring, maintaining, and troubleshooting a site’s presence in Google Search.
GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)
New approaches for optimizing content to appear in answers/overviews generated by AI-driven search engines.
H
Header Tags (H1–H6)
HTML tags for structuring content hierarchically (H1 is most important).
HTTPS
Secure protocol for website data transfer, a ranking factor.
I
Indexing
The process by which search engines store and organize web content for retrieval.
Internal Link
A hyperlink from one page to another page within the same website.
J
JavaScript SEO
Best practices for ensuring content rendered by JavaScript is discoverable and indexable by search engines.
K
Keyword
A word or phrase targeted in SEO to attract search traffic.
Keyword Research
The process of identifying valuable search terms for targeting.
Keyword Cannibalization
Multiple pages on a website competing for the same keyword, potentially undermining rankings.
Keyword Stuffing
The overuse of keywords in content in an attempt to manipulate rankings—considered a black hat tactic.
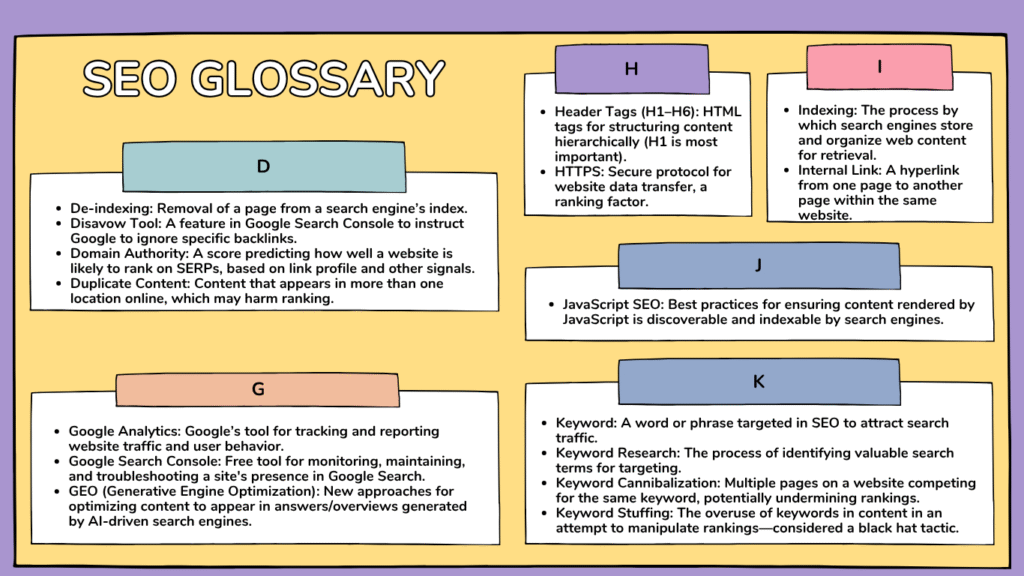
L
Landing Page
The first page a user arrives at from a search engine or ad.
Link Building
Activities aimed at acquiring backlinks to improve ranking authority.
Local SEO
Optimizing your online presence for local search queries (e.g., “near me”), including Google Business Profiles.
M
Meta Description
An HTML tag providing a summary of a web page’s content for display in SERPs.
Mobile-First Indexing
Google’s method of ranking and indexing content based on the mobile version of a site.
Manual Action
A penalty from Google for violating search guidelines.
N
Noindex
A tag that prevents search engines from indexing a page.
Nofollow
A value assigned to links telling search engines not to pass any ranking authority to the linked page.
O
On-Page SEO
Optimization work (content, structure, meta tags) done directly on your website.
Off-Page SEO
Optimization performed outside your website—primarily link building, PR, and brand mentions.
Organic Search
Unpaid search results that appear because of SEO efforts.
P
PPC (Pay-Per-Click)
Paid advertising model where advertisers pay for each click on their ads.
Page Speed
How quickly a page loads for users, important for UX and SEO.
Penalty
A negative impact on rankings due to violation of search engine policies.
Position Zero
The very top spot in Google search results occupied by featured snippets.
Q
Quality Content
Content that is original, helpful, authoritative, and satisfies search/user intent.
Query
The word or phrase entered into a search engine by a user.
R
Ranking
The position of a web page in search engine results.
Redirect (301/302)
A method of forwarding one URL to another—301 is permanent, 302 is temporary.
Robots.txt
A file that instructs search engines which pages to crawl or ignore.
Rich Snippet
Enhanced search results including additional data (reviews, FAQs, etc.).
ROI (Return on Investment)
The effectiveness and profitability of your SEO (or other marketing) campaigns.
S
Schema Markup
Code that helps search engines better understand content, improving your chance of rich results.
Scraping
Automated extraction of data/content from websites.
Search Engine
A program (like Google or Bing) that indexes and ranks content based on queries.
SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
Encompasses both SEO and paid search advertising (PPC).
SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
The process of improving visibility in organic search results.
SERP (Search Engine Results Page)
The page displaying results for a search query.
Sitemap
A file listing all pages on your site, aiding search engines in discovering and indexing content.
Site Audit
Comprehensive review of a website to identify SEO and technical issues.
Sitelinks
Additional links displayed below a main URL in search results, directing users to important subpages.
Spam
Unsolicited, irrelevant or manipulative content or links.
T
Thin Content
Pages with insufficient or low-value content.
Title Tag
The HTML title of a web page, visible in browser tabs and SERPs, and a key ranking factor.
Topical Authority
Recognition of a site or author as a trusted source on a given topic.
Traffic
The visitors coming to your site.
U
URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
The address of a web page.
UX (User Experience)
The overall experience a user has on a website, factoring heavily in SEO.
V
Voice Search
Search queries spoken aloud via devices (phones, smart speakers) requiring natural language optimization.
Visibility
How often and how prominently a site appears in search results.
W
White Hat SEO
Ethical SEO strategies following search engines’ guidelines.
Webmaster Guidelines
Official dos and don’ts provided by search engines for optimal practices.
X
XML Sitemap
A structured list of a website’s pages in XML format, submitted to search engines for improved indexing.
Y
YMYL (Your Money or Your Life)
Pages that impact a person’s finances, health, safety, or well-being—held to higher quality standards.
Z
Zero-Click Search
A query resolved directly on the SERP (e.g., answer boxes or AI overviews) where the user does not click through to a website.
Additional information could be found on the Google SEO starter guide!