Table of Contents
Next Steps & How to Get Started
What Is a Search Engine Optimization Agency & Why It Matters
SEO vs SEM vs PPC: Understanding the Differences
How an SEO Agency Operates: Technical, On‑Page & Off‑Page SEO
Specialized SEO Services: E‑commerce, Local, International, News & Enterprise
The SEO Process: Research, Planning, Implementation, Monitoring & Reporting
How to Choose the Right Agency: Top Questions to Ask
FAQs: Most Searched Questions About SEO Agencies
Search engine optimization agency experts know that visibility and credibility go together. Imagine your website appearing organically on page one, ahead of competitors—bringing qualified leads and profitable growth. In this story, you’ll discover how a strategic agency approach—not just technical fixes—can transform your search presence into a powerful engine for your business. Let’s explore how choosing the right partner can bring measurable impact, sustained momentum, and long‑term ROI.
SEO is considered a fundamental digital marketing practice that can be applied to any website. It helps improve a site’s visibility on search engines like Google and Microsoft Bing, regardless of whether your site promotes products, offers services, or shares expert knowledge on specific topics.
How SEO Differs from SEM and PPC
Understanding the relationship between SEO, SEM (Search Engine Marketing), and PPC (Pay-Per-Click) is crucial for developing effective digital marketing strategies.
SEO vs. SEM
SEM stands for search engine marketing and serves as an umbrella term for the combination of SEO and PPC activities. Think of SEM as a coin where SEO represents one side (organic results) and PPC represents the other side (paid results).
- SEO: Drives organic result clicks from search engines
- SEM: Drives both organic and paid result clicks from search engines
- PPC: Drives paid result clicks from search engines
SEO vs. PPC
PPC is a type of digital marketing where advertisers pay when users click on their ads. Advertisers bid on specific keywords to have their ads appear in search results.
Key differences include:
- With PPC, advertisers pay for each click on their paid listing
- With SEO, search result listings haven’t been directly paid for, though SEO requires time and investment
- SEO and PPC are complementary channels; ideally, you should use both when budget allows
Why SEO Is Important
SEO has become a critical marketing channel for several compelling reasons:
Massive Market Reach
- Organic search delivers 53% of all website traffic
- Google processes over 8.5 billion searches daily and owns 91% of the global search engine market
- 68% of online experiences begin with a search engine
Economic Impact
- The global SEO industry is forecast to reach $122.11 billion by 2028
- The SEO software market alone is projected to reach $265.91 billion by 2034
- 61% of B2B marketers say SEO and organic traffic generate more leads than any other marketing channel
Search Behavior Evolution
Modern search behavior is increasingly fragmented across platforms:
- 56% of U.S. online shoppers start product searches on Amazon
- 25% start on YouTube
- 19% each start on Instagram and TikTok
- Among Gen Z women, 51% prefer starting searches on TikTok over other sources
Competitive Advantage
Search engine results pages are highly competitive, filled with various SERP features including AI Overviews, knowledge panels, featured snippets, maps, images, videos, and more. The top result on Google captures 27.6% of all clicks, while only 0.63% of users go beyond the first page.
Types of SEO and Specializations
SEO can be conceptualized as a sports team where you need strong offense, defense, and fan engagement. This translates into three main types of optimization:
Technical SEO (The Defense)
Technical SEO focuses on optimizing the technical aspects of a website to ensure search engines can efficiently crawl, render, index, and rank your content.
Key Technical Elements:
- Website architecture and crawlability
- URL structure, navigation, and internal linking
- Core Web Vitals (page loading speed, interactivity, visual stability)
- Mobile-friendliness and responsive design
- HTTPS security
- Structured data (schema markup)
- XML sitemaps
- Site speed optimization
On-Page SEO (The Offense)
On-page SEO involves optimizing content and HTML elements on individual web pages for both users and search engines.
Content Optimization for Users:
- Coverage of relevant topics with experience or expertise
- Natural inclusion of keywords people use to find content
- Unique, original, and well-written content
- Up-to-date and accurate information
- Multimedia integration (images, videos)
- Superior quality compared to SERP competitors
- Clear structure with proper formatting
Technical Elements for Search Engines:
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- Header tags (H1-H6)
- Image alt text
- Open graph metadata
Off-Page SEO (Building the Fanbase)
Off-page SEO encompasses activities outside your website that build brand assets and demonstrate expertise, authority, and trustworthiness.
Link Building Activities:
- Brand building and marketing to boost recognition
- Public relations for earning editorial links
- Content marketing (videos, ebooks, research studies, podcasts, guest posting)
- Social media marketing and optimization
- Listing management across directories and review sites
- Ratings and reviews acquisition and management
SEO Specializations
Different industries and business models require specialized SEO approaches:
- E-commerce SEO: Product pages, category optimization, faceted navigation, schema markup
- Enterprise SEO: Large-scale optimization for websites with 1+ million pages
- International SEO: Multi-regional and multilingual website optimization
- Local SEO: Optimization for local search visibility and Google My Business
- News SEO: Fast indexing and appearing in Google Discover, Top Stories, and Google News
How SEO Works
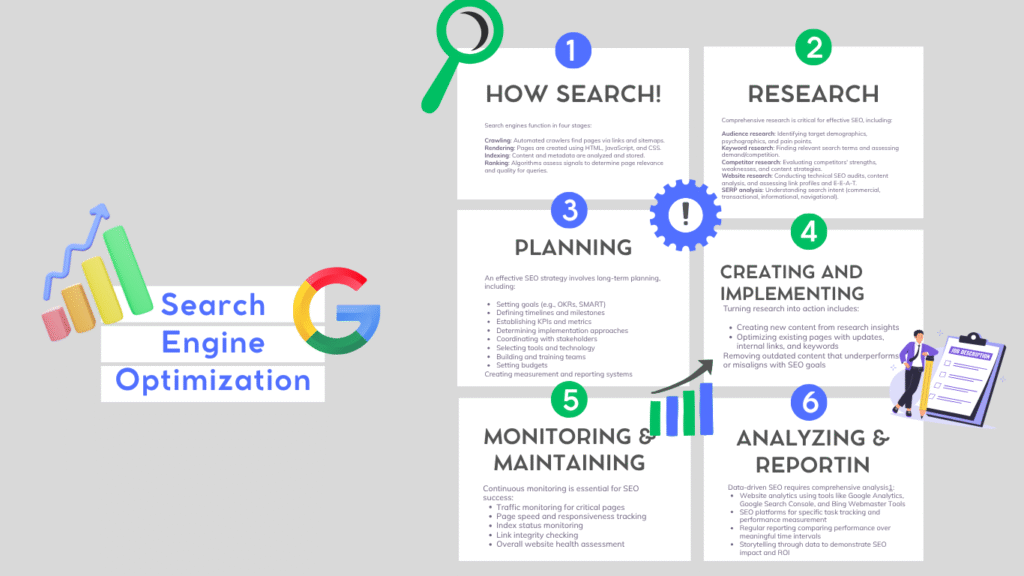
SEO success results from the coordination of four key components: People, Processes, Technology, and Activities. The process involves six critical areas working in combination:
1. Understanding How Search Engines Work
Search engines operate through four distinct stages:
- Crawling: Search engines use automated programs (crawlers/spiders) to discover pages by following links and using sitemaps.
- Rendering: Search engines generate how pages will look using HTML, JavaScript, and CSS information.
- Indexing: Search engines analyze content and metadata, storing information in their database. Not every discovered page gets indexed.
- Ranking: Complex algorithms evaluate various signals to determine page relevance and quality for specific search queries.
2. Research
Comprehensive research forms the foundation of effective SEO:
- Audience research
- Keyword research
- Competitor research
- Website research
- SERP analysis
3. Planning
An effective SEO strategy requires long-term planning:
- Setting goals (OKRs, SMART)
- Defining timelines and KPIs
- Implementation planning
- Team coordination
- Budget and tools
4. Creating and Implementing
Turning research into action involves:
- Creating new content
- Optimizing existing content
- Removing outdated or low-performing content
5. Monitoring and Maintaining
Continuous monitoring is essential:
- Traffic monitoring
- Speed and responsiveness
- Index status and link integrity
- Health checks
6. Analyzing and Reporting
Data-driven SEO requires:
- Analytics tools (Google Analytics, Search Console, Bing Webmaster)
- SEO platforms for task tracking
- Storytelling with data to show ROI
How SEO Evolves
SEO constantly evolves due to technological advances and societal changes:
Adapting to Technology
- AI-Driven Search Results
- Mobile-First Indexing
- Speed and UX
Adapting to Society
- Macroeconomic Factors
- Pandemic Impact
SEO as a Service and Career
The SEO industry represents a significant economic opportunity:
Market Growth:
- From $75.13B (2023) to $88.91B (2024)
- Projected to reach $170B by 2028
- SEO content creation market: $26.2B → $88.6B by 2032
Career Opportunities:
- 65% in-house, 35% agency
- 59% mid-level roles
- 12% offer $100K+
- Key skills: AI, UX, data analytics
Career Progression Path:
- Entry Level: SEO Apprentice/Trainee
- Junior Level: SEO Specialist
- Mid-Level: Senior SEO Specialist
- Senior Level: SEO Manager
- Leadership: SEO Director/Head of SEO
Learning SEO
SEO education requires continuous learning:
Essential Learning Resources
Free Educational Platforms:
- Ahrefs SEO Course
- LearningSEO.io
- Semrush Academy
- Google tools
Recommended Learning Path:
- Master fundamentals
- Develop technical skills
- Practice hands-on
- Stay updated
- Specialize
Key Skills for 2025
Modern SEO professionals need diverse skills:
Technical Skills:
- Site architecture, Core Web Vitals
- Schema markup
- Mobile optimization
- AI tool integration
Strategic Skills:
- Content strategy
- Link building
- Analytics
- Local SEO
Emerging Skills:
- AI and automation
- Voice search
- Visual search
- Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
The Future of SEO
SEO remains a critical digital marketing discipline:
Key Trends Shaping SEO’s Future:
- AI and machine learning
- UX and Core Web Vitals
- Voice and visual search
- E-E-A-T
- Search experience optimization
Success Factors for 2025 and Beyond:
- High-quality content
- Technical excellence
- Link authority
- Continuous learning
- Strategic alignment
The Bottom Line
There are no universal truths or secrets in SEO.
Success requires consistent effort across all phases of SEO to grow visibility, traffic, authority, conversions, and revenue.
As the digital landscape continues evolving, SEO professionals who combine technical expertise with strategic thinking and continuous learning will find the most success in this dynamic field.
FAQ Section:
Q: What should I ask before hiring an SEO agency?
Ask about their experience, case studies, SEO strategy, tools, how you’ll communicate, pricing, timelines, deliverables, and whether they’ve worked with competitors.
Q: How do agencies define SEO success?
They define success by metrics tied to your goals—organic traffic, conversions, revenue—not just rankings or vanity stats. Expect regular reporting on KPIs like traffic, leads, and conversions.
Q: When will I see results from SEO efforts?
Results usually take several months; typical timelines range from 3–6 months before meaningful rankings and traffic improvements appear.
Q: What questions reveal the right SEO process?
Ask them to walk you through their process: discovery, planning, audits, optimization, content strategy, link-building, integration with your marketing mix.
Q: Do they specialize in my industry or offer local/international SEO?
Specialization means faster, more effective strategies. Ask if they’ve worked in your industry or region, and about experience with local search or multi-regional sites.
Q: Do they use white‑hat SEO and stay up to date?
Good agencies avoid black-hat tactics. They stay current via industry blogs, Google updates, and major SEO forums. Ask how they monitor algorithm changes.
Q: How much involvement from my team is needed?
Clarify resource needs: onboarding, audits, content approvals, meetings. Good agencies involve clients appropriately and make collaboration clear